12+ Nucleus Of Plant
The DNA housed within the cell nucleus contains the information necessary for the creation of the majority of the proteins needed to keep a. Web In the first part of the review we briefly assess the traditional roles of the plant nucleolus in rRNA synthesis and ribosome biogenesis as well as possible functions in other RNA regulatory pathways such as splicing nonsense-mediated mRNA decay and RNA silencing.

Cell Structure Grade 9 Understanding For Igcse Biology 2 2 2 3 2 4 Pmg Biology
1 It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis which is the synthesis of ribosomes.

. Then where an animal cell would go through cytokineses a plant cell simply creates a new cell plate in the middle creating two new cells. Instead their DNA is in a region called the nucleoid. Beyond the rough endoplasmic reticulum is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum.
A typical plant cell is around 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter while a bacterial cell is. 1 the stomatal file is specified from undifferentiated epidermal cells. The nucleus controls and regulates the activities of the cell eg growth and metabolism and carries the genes.
Nuclei is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Nucleus of a cell showing the nucleolus in the centre of the nucleus and the nuclear membrane. Nucleolus plays a significant role in.
Web Here we review what is known about the control of nuclear shape and size in the Archaeplastidae the supergroup containing the higher plants. The nuclear membrane has numerous pores to allow communication with the rest of the cell. All cells have a cell membrane that separates the inside and the outside of the cell and controls what goes in and comes out.
Cells contain parts called organelles. Learn about the plant cell nucleus including its structure. Web Plant genomes are organized in three dimensions through interactions with landmarks within the nucleus including the nucleolus and the nuclear periphery as well as self-organizing foci such as heterochromatic aggregates.
A A maize seedling showing the developmental gradient of an emerging leafB Schematic representation of stomata development at the base of the leaf. Web Developmental trajectory of maize stomata and MLKS2-mediated nuclear positioning and division plane specification. Cell Wall Plasma Membrane and Middle Lamella.
Web The nucleolus njuːˈkliːələs ˌnjuːkliˈoʊləs. Web Parts of the Plant Cell Nucleus Chromatin. Nucleoli - laɪ is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
Hard on the heels of President Joe Bidens. Web Do plant cells have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus but a few cell types such as mammalian red blood cells have no nuclei and a few others including osteoclasts have many.
The cell membrane surrounds a cells cytoplasm which is a jelly-like substance containing the cells parts. The nucleus also has a protective effect on the. Plant cells are generally much larger than bacterial cells.
It is also connected to the rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane system. In plants these essential organelles occur in all green. Web Plant cell the basic unit of all plants.
Web Cartoon showing a close up the nucleus and highlighting structures specific to the nucleus. See the nucleus function in a plant cell and compare to animal cells. Web The US Department of Energy said Thursday it plans to fuel the auto industrys transition to electric vehicles with 12 billion in loans and grants.
Web In plant cells the first part of mitosis is the same as in animal cells. Plant cells have a well-defined nucleus that houses their DNA. 48 49 EDS1- PAD4- SAG101-containing.
A nucleus has interesting implications for how a cell responds to its environment. Chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll to absorb light energy. We discuss common themes as well as differences toward a more generalized model of how eukaryotic organisms regulate nuclear morphology.
Web The cell nucleus is a large organelle in eukaryotic organisms which protects the majority of the DNA within each cell. It appears as a spherical mass that lacks a membrane around it. Chromatin carries the DNA in a much-condensed form because of the large content of the DNA that carries gene.
Web Nucleus in biology a specialized structure occurring in most cells except bacteria and blue-green algae and separated from the rest of the cell by a double layer the nuclear membrane. Web nucellus plant anatomy Learn about this topic in these articles. Plant cells like animal cells are eukaryotic meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Assorted References development of seed and fruit In seed. Web The nucleus contains most of the genetic material excluding the mitochondrial and in plants the chloroplastic genomes Figure 1. Inside the nucleus chromatin DNA wrapped around proteins described further below is stored in a gel-like substance called nucleoplasm.
Their characteristic cell wall is composed of cellulose and they contain chloroplasts for. Angiosperm seedspart a region called the nucellus that in turn contains an embryo sac with eight nuclei each with one set of chromosomes ie they are haploid nuclei. Thanks to the added protection of the nuclear envelope the DNA is a little bit more secure from enzymes pathogens and potentially harmful products of fat and protein.
Web The plant immune regulator EDS1 enhanced disease susceptibility1 is a master component of plant defense 47 48 that transiently associates in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus with its co-regulator partners PAD4 Phytoalexin Deficient4 and SAG101 Senescence-Associated Gene101. Web High school biology Cells Plant vs animal cells 2023 Khan Academy Privacy Policy Cookie Notice Plant vs animal cells review Google Classroom How do plant and animal cells differ. Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase.
Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. Web The nucleus plural nuclei houses the cells genetic material or DNA and is also the site of synthesis for ribosomes the cellular machines that assemble proteins. Web The cell nucleus from Latin nucleus or nuculeus kernel seed.
Web A chloroplast is a type of plastid a saclike organelle with a double membrane that serves as the site of photosynthesis the process by which energy from the Sun is converted into chemical energy for growth. Functionally it separates the DNA replication and DNA transcription taking place in the nucleoplasm from the protein translation in the cytosol. Web The shape of the nucleus has been assessed both by labelling internal components for instance chromatin and by labelling membranes including the NE or endoplasmic reticulum in interphase cells and viral-infected cells of plants.
The cell plate later changes to a cell wall once the division is complete. Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic so they contain membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria. The nucleus also produces the necessary precursors for protein synthesis.
In contrast bacterial cells do not contain a nucleus.
Nucleus Of A Cell Where Is The Nucleus Located Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
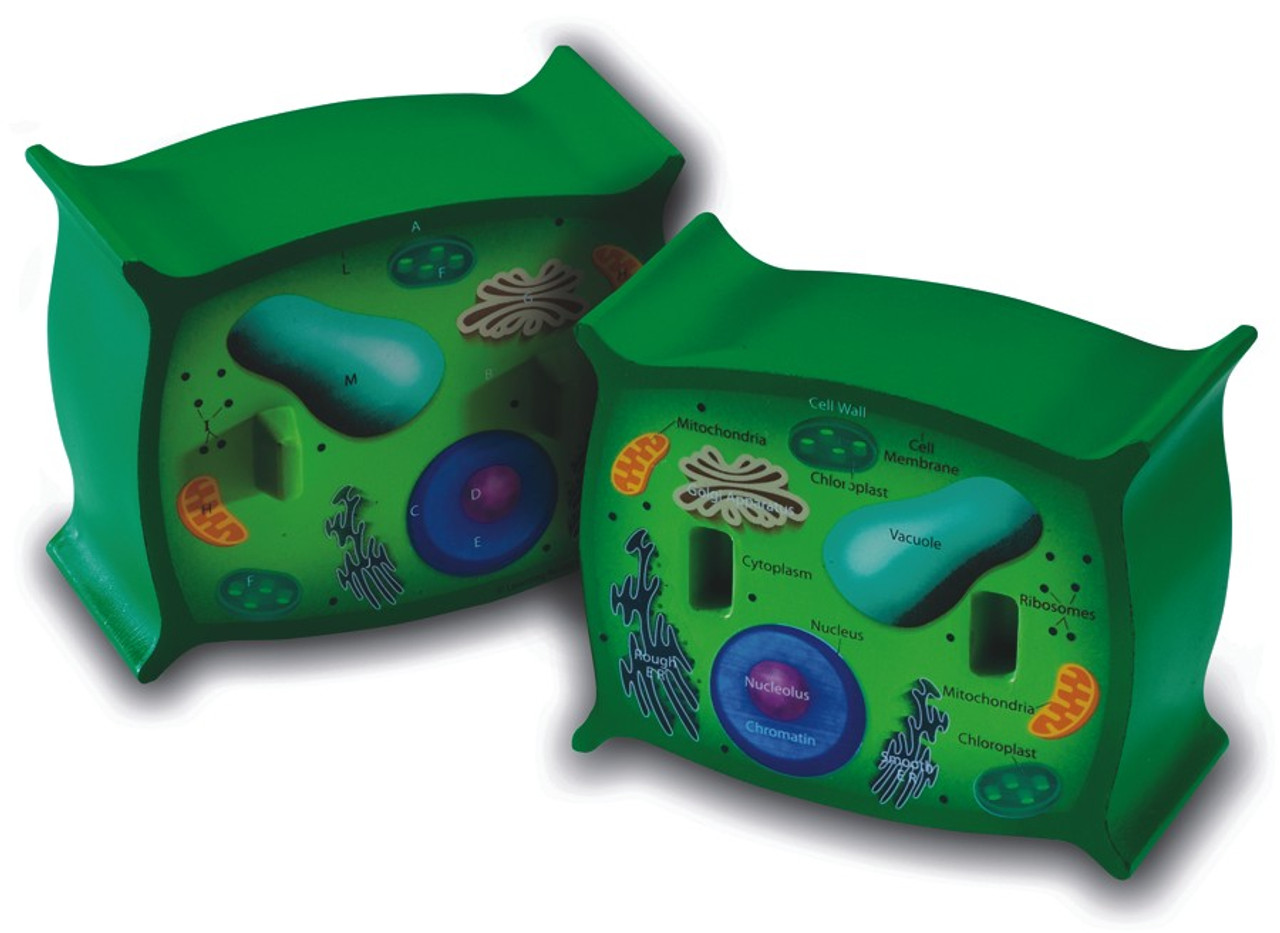
Plant Cell Model Labeled Unlabeled Halves

Biology 11th Class Chapter 4 Nucleus Learning With Qais Youtube
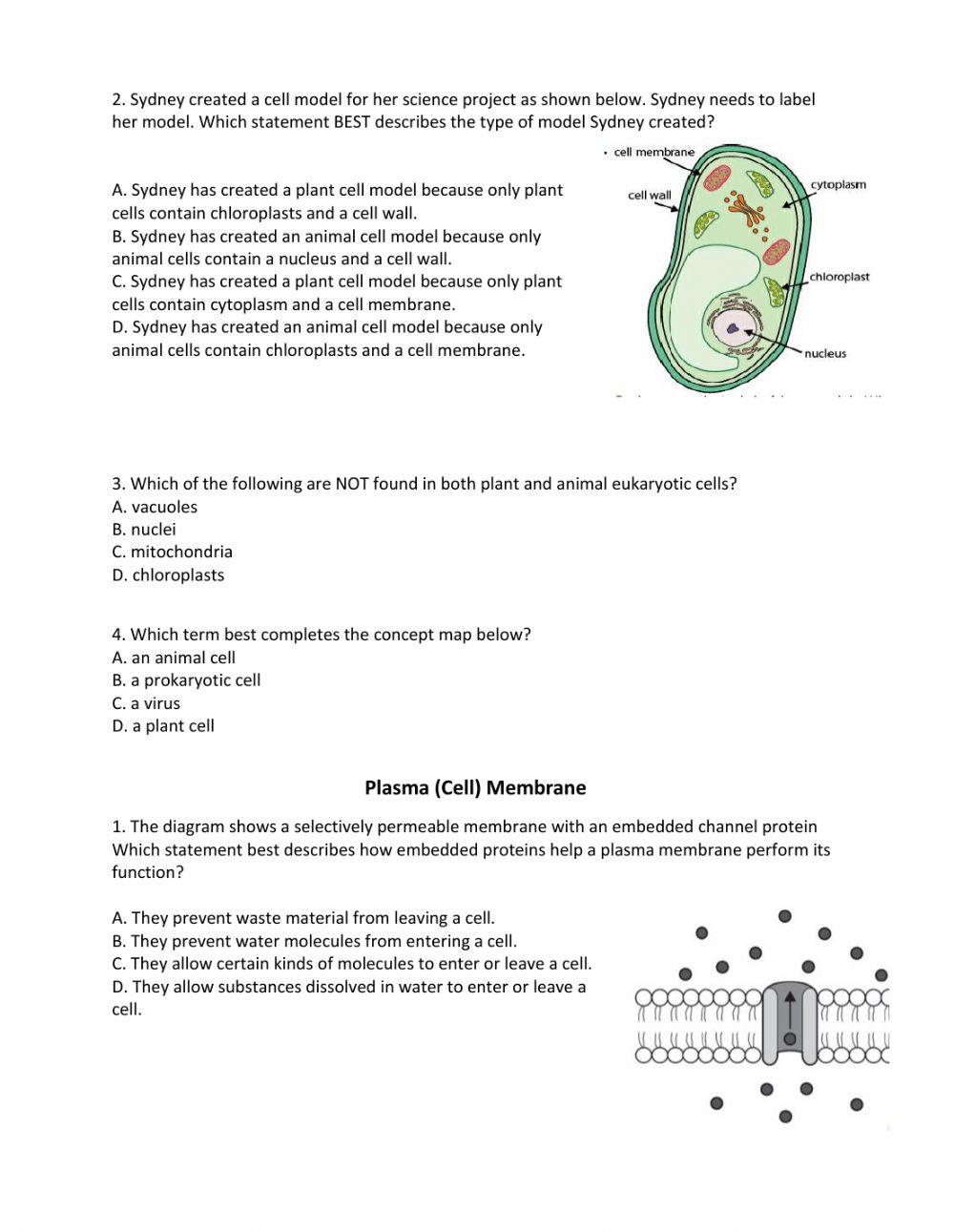
Unit 1 Assessment Activity Live Worksheets
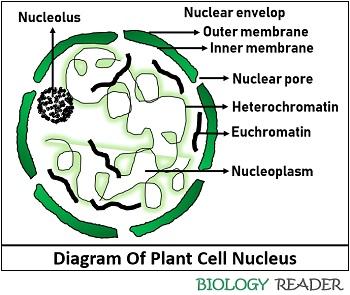
What Is Plant Cell Nucleus Meaning Structure Parts Functions Biology Reader
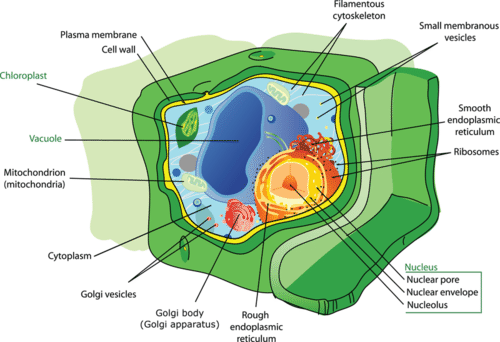
Plant Cell Structure Ck 12 Foundation

Crossover Analysis In Male Meiocytes Of Wild Type Mpg And Recq4 Download Scientific Diagram

Plant Cell Nucleus Definition Function Structure Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
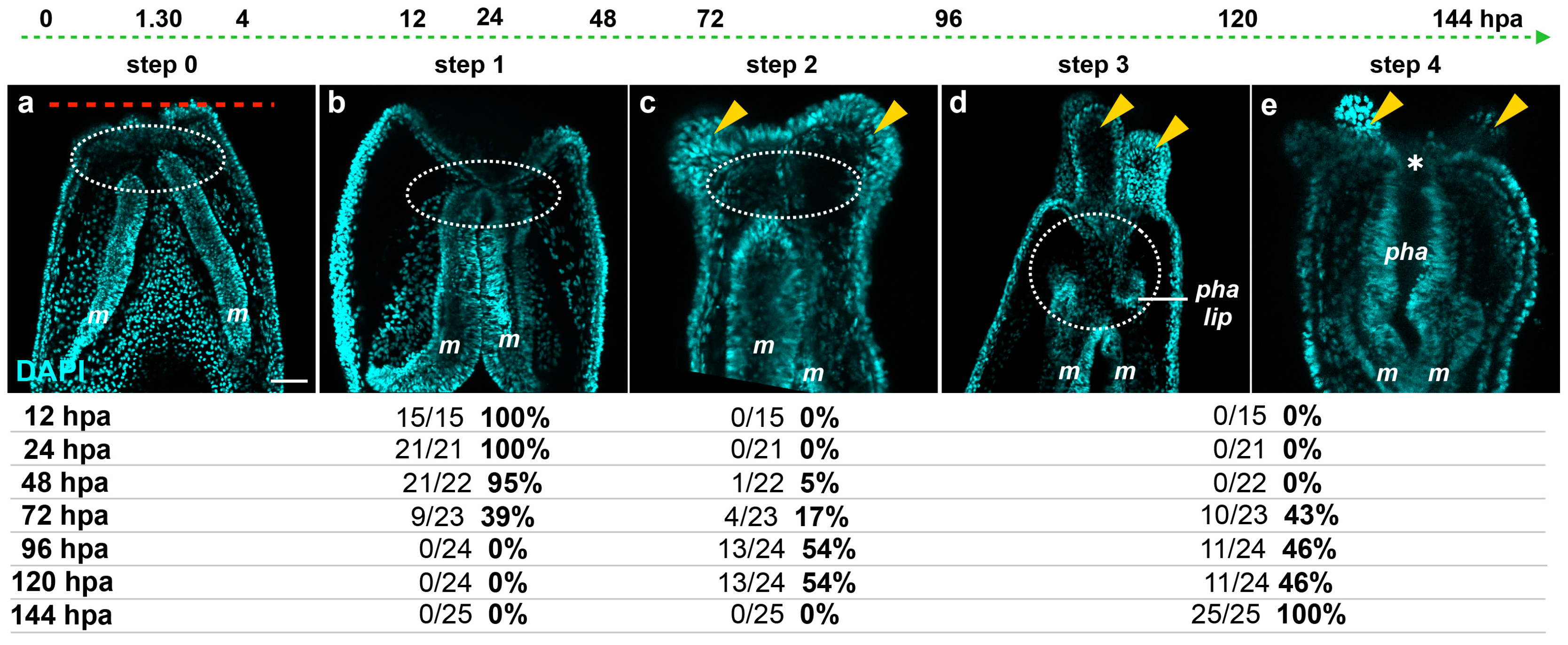
Ijms Free Full Text Characterization Of Morphological And Cellular Events Underlying Oral Regeneration In The Sea Anemone Nematostella Vectensis
Age Related Changes In Eye Lens Biomechanics Morphology Refractive Index And Transparency Aging
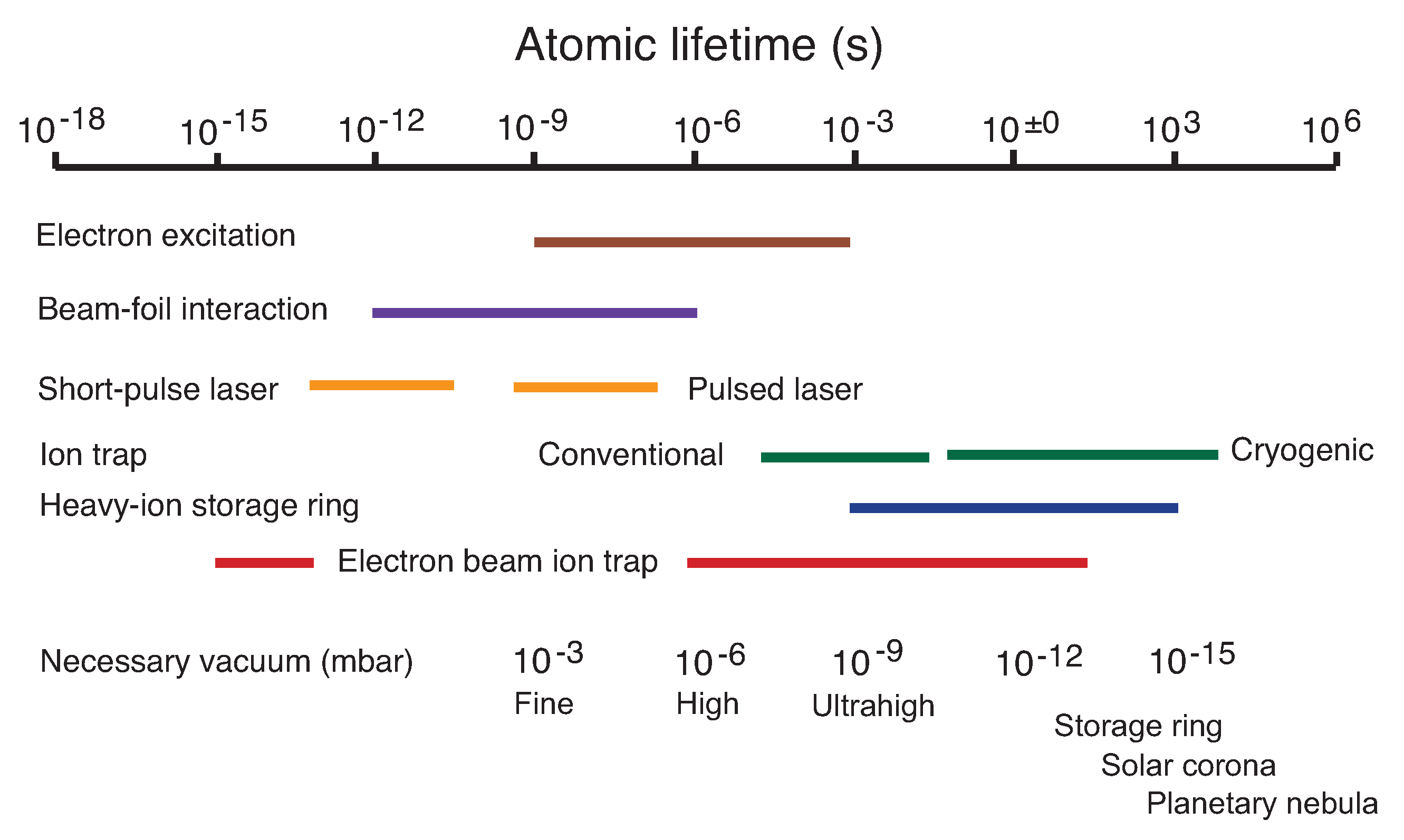
Atoms Free Full Text On Atomic Lifetimes And Environmental Density

4 222 Plant Cell Nucleus Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock

Plant Cell

Plant Cell 3d Model By Zulhilmi Zakaria Zulhilmi Zakaria 90370b9

Y52bn8p8zg1pcm

Cell Nucleus Definition Structure Function With Diagram
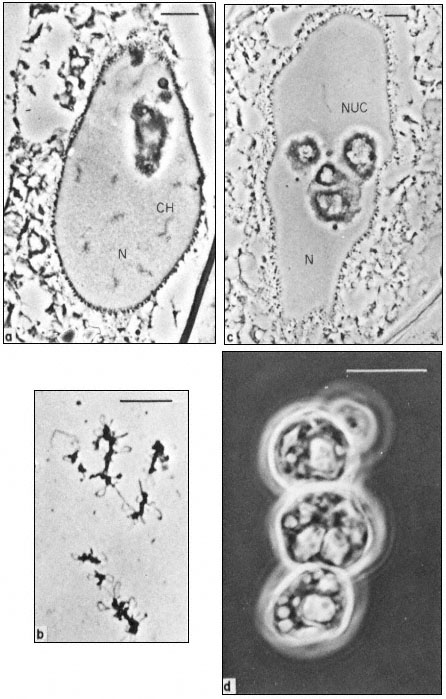
The Molecular Biology Of Plant Cells